
Punctate colonies are another name for small colonies (pin-point). A representative colony’s diameter can be expressed in relative terms like pinpoint, small, medium, and big or in millimeters.īacterial colonies that are punctiform and various shapes The colony’s size may be a helpful characteristic for identification. and other highly mobile species inundated the culture media. Examples of thisĬolonies with uneven shapes and/or edges are probably made up of mobile creatures. The edge or margin of a bacterial colony may be a key element in determining an organism’s identity. There are six main bacterial colony elevations: This is how a colony appears from the “side.” These four types are the most typical colony shapes you will probably see.Įlevation of the bacterial colony: It reveals the colony’s height above the agar. The shape of the bacterial colony is referred to as its form. It includes the bacterial colony’s shape, elevation, and margin. Alpha – Blood cells are partially destroyed.Accordingly, the bacterial colony could be: Haemolysin, a substance made by some bacteria, causes hemolysis close to the colony.Transparent, translucent, or opaque describes opacity.Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces the pigments pyoverdin and pyocyanin, which give the colonies a greenish sheen. Serratia marcescens produces the orange-red pigment known as prodigiosin. Color – Specific bacterial species create pigments.Edges might be whole, lobate, crenate, undulate, or ciliate.
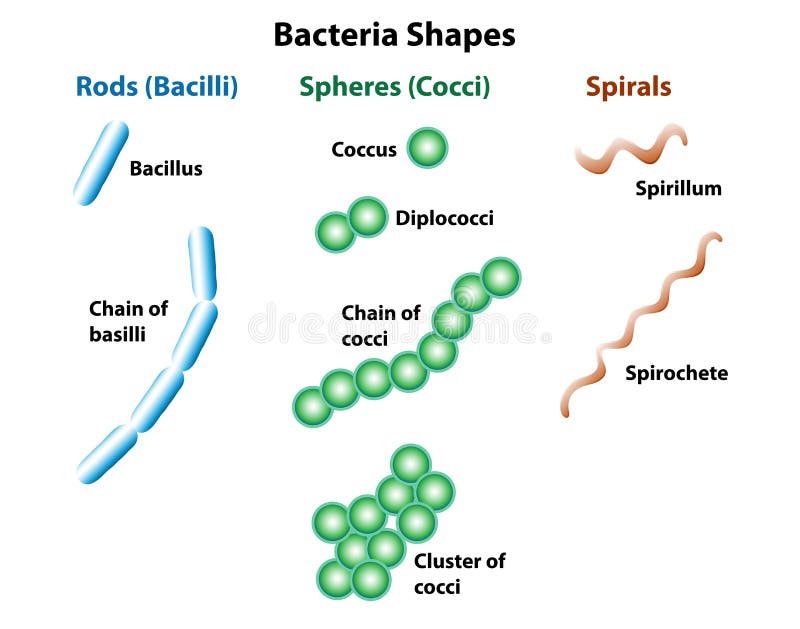
Colonies can be elevated, flat, convex, umbonate, pulvinate, or crateriform depending on their elevation.Shapes that are irregular, rhizoid, filamentous, or spherical.Brittle/friable (dry, breaks apart), firm, butyrous (buttery), and mucoid are the four different types of texture (sticky, mucus-like).Size: The diameter of a sample bacterial colony is measured in millimeters and size ranges from large (>1 mm), medium (=1 mm) and, small (1 mm), to pinpoint (0.5 mm).Surfaces could be grainy, glossy, rough, drab, or wrinkled. The bacterial colony frequently exhibits the following characteristics.

Morphological features of a colonyįrequently, the appearance of the bacterial colony on the culture media serves as the identifying trait for a particular bacterial species and bacterial morphology. The visual qualities of a bacterial colony on an agar plate are known as a colony.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
